GC-MS analysis
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is a popular and versatile analysis technique for identifying and quantifying concentrations of organic substances. Common applications of GC-MS include quality control in the food industry, impurity screening of environmental samples, and food contact material migration testing.

Some of our GC-MS services
Specific migration testing – non-intentionally added substances (NIAS), GC-MS
PFAS in plastic, paper, and other solid materials (165 compounds)
Printing ink set-off testing with GC-MS
Pesticide residue screening (extensive package)
Specific migration testing – Irganox 1076 (CAS: 2082-79-3)
Specific migration testing – ethylene glycol and diethylene glycol
Specific migration testing – acetaldehyde (CAS 75-07-0)
Specific migration testing – 9,9-bis(methoxymethyl)fluorene
Prices excluding VAT.
What is GC-MS used for?
GC-MS and its high-sensitivity version, GC-MS/MS, are commonly used to screen different types of samples for volatile and semi-volatile organic contaminants, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), phthalates, and pesticides. Applications for which Measurlabs offers GC-MS analyses include the following:
NIAS testing of food contact materials, which involves screening the sample for non-intentionally added contaminants without prior information about which compounds are present.
Chemical characterization of substances released from medical devices (extractables & leachables testing).
Residual monomer quantification in polymeric materials (with complementary methods, such as HPLC and NMR, if necessary).
Phthalates analysis of toys, food packaging, and consumer products.
Printing ink set-off testing to measure the concentration of chemicals transferred to the food contact side of printed articles during storage.
Volatile organic compound (VOC) screening of water and other environmental samples.
PAH analysis of food, water, paper, plastics, textiles, and rubber.
Various food industry quality control analyses, including fatty acid profile determination, dioxin and PCB screening, and ethylene oxide residue testing.
As GC-MS is an exceptionally versatile method, the above are just some examples of popular applications. Do not hesitate to contact us to discuss your analysis needs.
How does the method work?
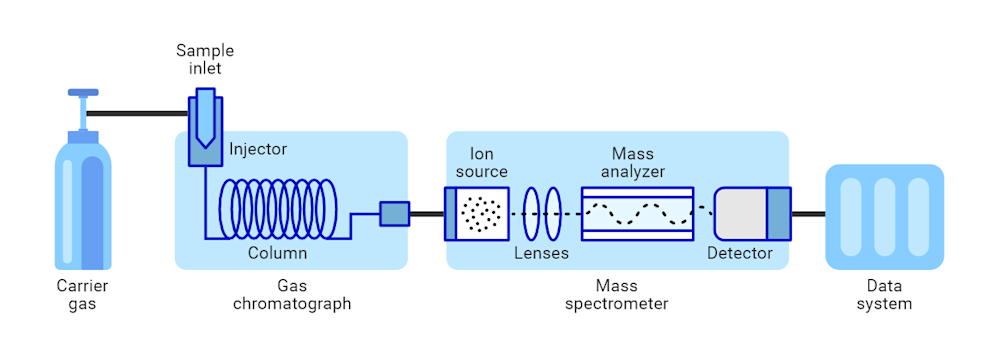
In GC-MS, the sample is first vaporized and injected into a gas chromatography (GC) column that is coated with a stationary phase. The column is heated, and an inert gas (the mobile phase) carries the sample through it. Compounds with distinct boiling points and polarities interact with the stationary phase in different ways, which leads to their separation and elution from the column at different retention times (RT).
The separated compounds are transferred to a mass spectrometer (MS), where they are ionized and fragmented. The ions are further separated based on their mass-to-charge (m/z) ratios using a magnetic or electronic field. As a result, a mass spectrum, with peaks corresponding to different compounds, is generated. By comparing the data on retention time and (m/z) ratios to existing standards, it is possible to identify and quantify compounds present in the sample.
Suitable samples for GC-MS
GC-MS is well-suited for detecting various types of molecules in a wide variety of sample matrices. A requirement is that the compounds in the sample are volatile or semi-volatile so that they can be separated from each other with a gas chromatograph and identified by a mass spectrometer. Many gaseous, liquid, and solid samples are suitable for GC-MS analysis without significant pretreatment. However, the analysis of complex samples or very small sample amounts may require more preparation.
Sample preparation
Gases and very easily volatile samples can be analyzed by collecting the substances of interest with the help of solid-phase microextraction (SPME). Then the compounds can be released into the gas chromatograph for analysis. Low-volatility compounds can be made more volatile through derivatization, where a chemical group, such as methyl or silyl, is attached to the target compound to lower its boiling point.
To examine samples that contain significant amounts of non-volatile matter, a headspace (HS) autosampler can be used. The sampler dispenses gas into the gas chromatograph from the top of the actual test sample, making it possible to analyze volatile compounds originating from non-volatile samples, such as soil or construction materials.
Yet another option is to apply the QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe) method to complex matrices to simplify sample extraction and cleanup. The method is most commonly used to analyze pesticide residues and mycotoxins in food industry samples.
The analysis can also be started with pyrolysis, i.e., breaking the sample through exposure to heat. The resulting py-GC-MS analysis is well-suited for analyzing polymeric materials, lignin, and other complex sample types. A GC-MS setup may also be connected to a thermogravimetric analyzer to analyze the evolved gases that are formed when the sample is heated.
Need an analysis?
Measurlabs offers a comprehensive selection of purity and composition analyses using GC-MS and related gas chromatography methods, such as GC-ECD and GC-FID. Whether it’s just a dozen or up to hundreds of samples, we offer competitive pricing and deliver reliable results quickly. Should you need assistance with method selection, our testing experts are always here to help craft testing plans and offer their best recommendations. Contact us using the form below to start the discussion and get a quote for your samples.
Suitable sample matrices
- Unknown organic materials
- Pure chemicals and different mixtures
- Food and beverage
- Fuels, oils and lubricants
- Environmental samples
Ideal uses of GC-MS
- Analysis of unknown organic compounds and mixtures
- Food and beverage safety testing to identify harmful compounds and determine their concentrations
- Compositional analysis of oils, fuels, and lubricants, e.g. PAH analysis
- Environmental tests, such as impurity screening of air, water, and soil samples
Ask for an offer
Fill in the form, and we'll reply in one business day.
Have questions or need help? Email us at info@measurlabs.com or call our sales team.
Frequently asked questions
GC-MS is most commonly used for separating and identifying different compounds from a complex mixture of substances as well as determining their quantities. GC-MS can be used, for instance, to screen food products for toxins or to determine the amount of volatile organic compounds in natural gases. The method can also be used to test petroleum products in the oil refining industry to find PAHs and to perform environmental tests on water, soil, and air samples to detect POPs and other contaminants.
When the compounds contained in the sample are known and only their concentrations are to be determined, gas chromatography alone is sufficient to obtain the results. However, if the composition of the sample is unknown, mass spectrometry is needed to identify the compounds. In this case, GC-MS should be used.
The compounds that are examined must be volatile or semi-volatile for gas chromatography to work. The sample matrix must be free of non-volatile substances, or a suitable method must be used to prevent the non-volatile matter from entering the gas chromatograph (HS-GC-MS, TD-GC-MS, SPME-GC-MS, or similar).
Liquid chromatography methods (HPLC-MS, HPLC-DAD) can be used to identify non-volatile substances that are not suited for GC-MS analysis.
GC-MS is a suitable method for analyzing gaseous, liquid, and solid samples. Gaseous and solid samples, as well as liquid samples containing non-volatile matter, require pretreatment and/or the use of a special autosampler prior to the analysis. Very complex samples containing many different substances can be analyzed with this method combination, but they must first be separated from possible non-volatiles, such as dirt.
Measurlabs offers a variety of laboratory analyses for product developers and quality managers. We perform some of the analyses in our own lab, but mostly we outsource them to carefully selected partner laboratories. This way we can send each sample to the lab that is best suited for the purpose, and offer high-quality analyses with more than a thousand different methods to our clients.
When you contact us through our contact form or by email, one of our specialists will take ownership of your case and answer your query. You get an offer with all the necessary details about the analysis, and can send your samples to the indicated address. We will then take care of sending your samples to the correct laboratories and write a clear report on the results for you.
Samples are usually delivered to our laboratory via courier. Contact us for further details before sending samples.