Dynamic light scattering
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) is a non-destructive method used to characterize particle or colloid size distributions in a solution. The typical measurement range is from around 0.3 nm to 10 µm.

Some of our most popular particle size distribution analyses
Particle size distribution with TEM
Particle size distribution using dynamic light scattering (DLS)
Particle size distribution with SEM
Particle size distribution by laser diffraction (dispersions)
Particle size distribution analysis according to EC recommendations
Particle size distribution by laser diffraction (dry mode analysis)
Particles size and shape analysis with image analyzer
Droplet size analysis for sprays
Prices excluding VAT.
What is dynamic light scattering used for?
Dynamic light scattering is used to determine the size distribution of particles in solution or suspension. It can also be used in polymer characterization to determine the hydrodynamic radius of the equivalent sphere for polymer chains.
DLS is widely used for particle size distribution analysis in food and feed, cosmetics, construction materials, and pharmaceuticals, among many other industries. The technique can also be used to characterize the size of proteins, carbohydrates, and other macromolecules.
How does DLS analysis work?
The principle of DLS is based on the theory of Brownian motion, which states that particles move randomly in a liquid or gas medium. During the analysis, the sample suspension is illuminated by a laser beam, leading to the laser light scattering in all directions as it hits the suspended particles. As smaller particles diffuse faster than larger ones, the measurement of the intensity fluctuation of the scattered light can be used to calculate the particle size distribution in the solution.
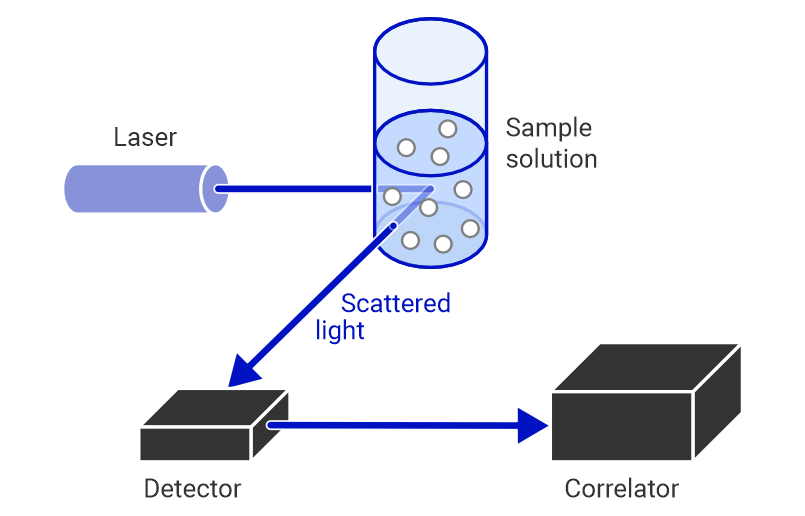
Suitable samples and sample preparation
DLS analysis is performed on liquid suspensions and dispersions. The typical detectable size range is 0.3 nm to 10 µm. If larger particles are present, they may affect the reliability of the results.
Strengths and limitations
The main strength of DLS compared with other particle size analysis methods, such as laser diffraction (LD), is the ability to analyze nanometer-scale particles. Other advantages include a relatively simple sample preparation procedure and the speed of the analysis. The main limitation of DLS is the assumption that particles are spherical, which may lead to uncertainties when determining the size of particles with very different shapes. Microscopy techniques, such as TEM or SEM, can help obtain more precise information about the shape and size of particles.
Need a DLS analysis?
Measurlabs offers particle size distribution measurements with DLS and other techniques, including laser diffraction, nanoparticle tracking analysis, sieve analysis, particle size and shape analysis, and electron microscopy. We handle even large sample batches with speed and precision, enabling you to get the insights you need without unnecessary delays. If you need help selecting the right method, our experts can recommend a suitable approach and assist with test planning. Use the form below to contact us.
Suitable sample matrices
- Liquids and suspensions
- Inks and pigments
- Microemulsions
- Protein and polymer samples
Ideal uses of DLS analysis
- Analyzing the hydrodynamic size and the size distribution of nanoparticles and molecules
- Determining the size of proteins, polymers, micelles, carbohydrates and nanoparticles
Ask for an offer
Fill in the form, and we'll reply in one business day.
Have questions or need help? Email us at info@measurlabs.com or call our sales team.
Frequently asked questions
Dynamic light scattering is used to analyze hydrodynamic particle size and size distributions in several industries and research areas, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, nanotechnology, and biomedical sciences.
DLS analysis assumes particles to be spherical, which makes it less suitable for other shapes, such as rods and fibers.
DLS samples can be liquids or solids that can be suspended in a suitable solvent.
Measurlabs offers a variety of laboratory analyses for product developers and quality managers. We perform some of the analyses in our own lab, but mostly we outsource them to carefully selected partner laboratories. This way we can send each sample to the lab that is best suited for the purpose, and offer high-quality analyses with more than a thousand different methods to our clients.
When you contact us through our contact form or by email, one of our specialists will take ownership of your case and answer your query. You get an offer with all the necessary details about the analysis, and can send your samples to the indicated address. We will then take care of sending your samples to the correct laboratories and write a clear report on the results for you.
Samples are usually delivered to our laboratory via courier. Contact us for further details before sending samples.