SIMS analysis
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) is a highly sensitive technique for compositional analysis and depth profiling of thin films, coatings, and other solid materials. It provides detailed information on elemental and isotopic distributions, impurity concentrations, and variations in chemical composition down to ppb levels. Due to its nanometer-scale depth resolution, SIMS is particularly valuable for analyzing ultra-thin layers, interfaces, impurity layers, and dopant profiles.

What is SIMS analysis used for?
SIMS is widely used to analyze a broad range of solid materials, including semiconductors, metals, oxides, and polymers. It is commonly used in the microelectronics and semiconductor industry to investigate doping profiles, trace contaminations, diffusion processes, and multilayer structures. The technique is especially useful for characterizing thin films deposited using methods such as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
One of the main advantages of SIMS is its ability to perform high-resolution compositional depth profiling, making it suitable for analyzing ultra-thin films and multilayer stacks with nanometer-scale precision. In addition, SIMS can detect and quantify all elements and isotopes, including hydrogen (H), in the parts-per-billion (ppb) and even parts-per-trillion (ppt) range. The technique can detect variations in composition across interfaces, making it valuable for studying diffusion, segregation, and interfacial layers.
While SIMS is an extremely powerful analytical tool, certain factors can affect its measurement accuracy. Matrix effects, preferential sputtering, and surface charging (especially in insulating materials) can influence ion yield and require careful calibration and interpretation. By optimizing analysis conditions, SIMS enables highly detailed chemical and isotopic insights into complex material systems.
What is the working principle of SIMS?
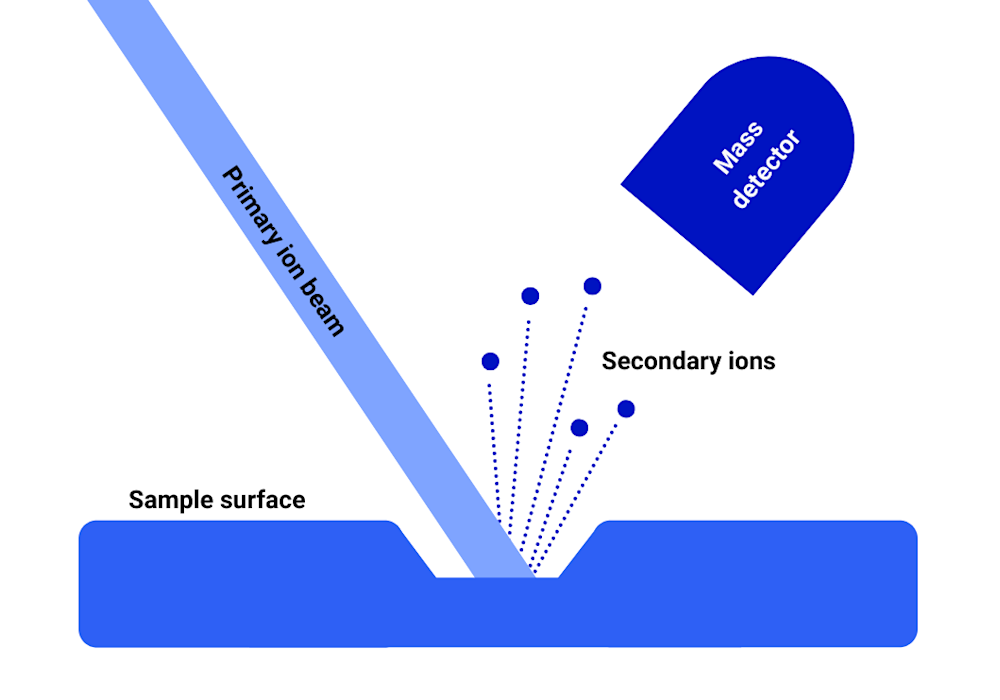
SIMS operates by bombarding a sample's surface with a focused beam of high-energy primary ions, such as oxygen (O2+) or caesium (Cs+). These primary ions transfer momentum to the sample atoms, ejecting secondary ions from the surface. The secondary ions are then collected and analyzed by a mass spectrometer to determine the sample's elemental, isotopic, and molecular composition.
During depth profiling, material is continuously removed from the surface, and variations in the composition are recorded, allowing for the analysis of interfaces, diffusion profiles, and ultra-thin layers. The depth resolution of SIMS depends on the energy of the primary ion beam. By adjusting the beam, we can create compositional depth profiles anywhere from a few nanometres to several microns.
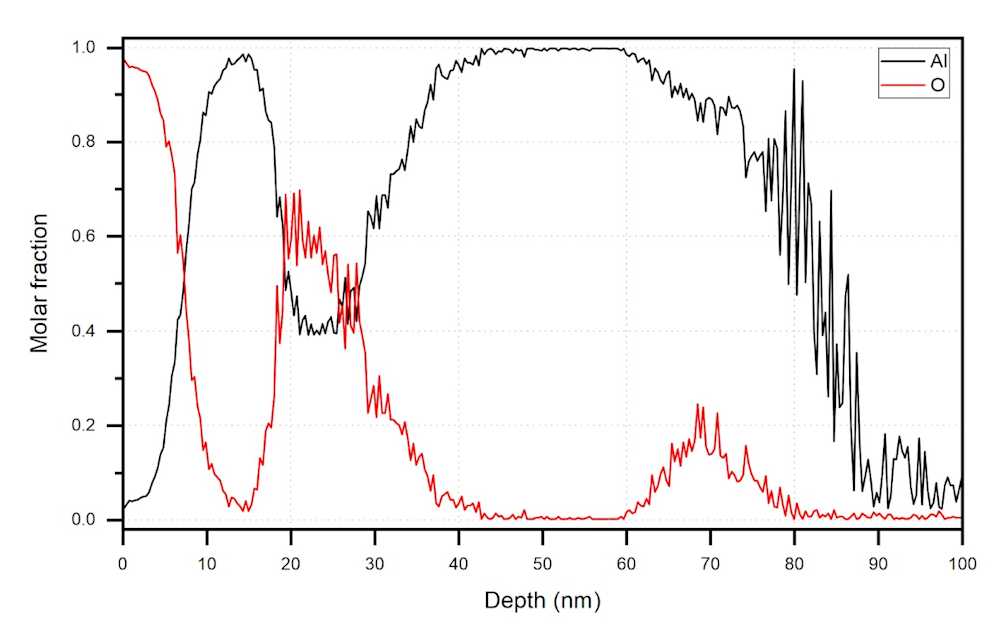
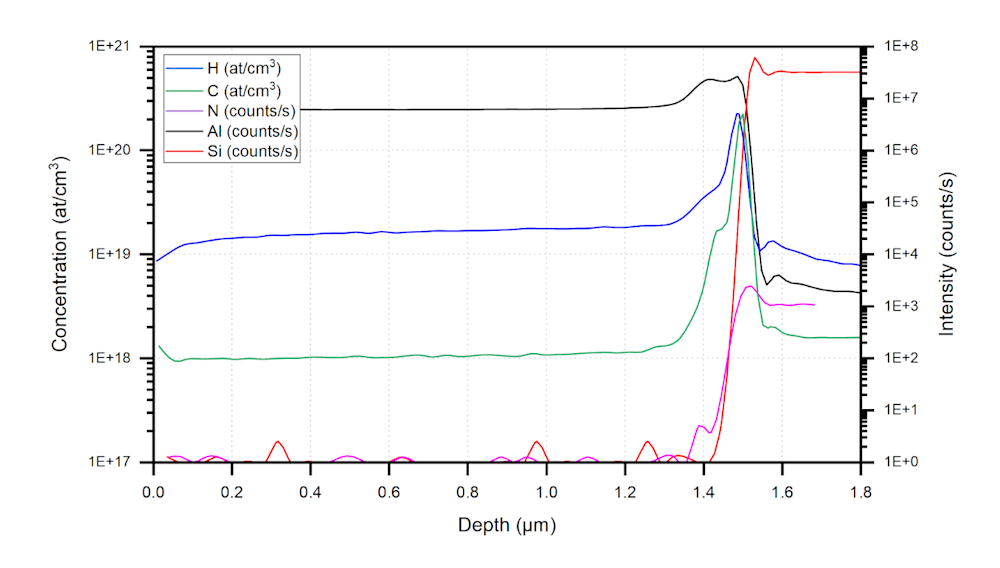
Examples of SIMS results
Static vs. dynamic SIMS
SIMS can be operated in two primary modes: static and dynamic. While both modes work on the same principle, they vary greatly in their primary ion beam type, equipment, and information that we can obtain from them.
Static SIMS (also known as ToF-SIMS) uses a low ion dose to probe only the topmost atomic layers (1-2 nm), allowing for high-sensitivity analysis of molecular and elemental composition on the outermost surface of the sample.
Dynamic SIMS (also known as SIMS) uses a continuous ion beam to progressively remove material from the surface, enabling high-resolution depth profiling of thin films, dopant distributions, and multilayer structures.
Need SIMS analyses?
Measurlabs offers laboratory testing with SIMS and ToF-SIMS techniques, with the capacity to handle large batches of samples and provide volume discounts for bulk orders. With fast turnaround times, access to various device types, and personalized service from method experts, Measurlabs is a trusted partner for over 700 clients in multiple industries, including Okmetic and other industry leaders in the semiconductor field.
Method Expert
Suitable sample matrices
- Bare wafers, such as silicon (Si), gallium nitride (GaN), silicon carbide (SiC), silicon oxide (SiO2), gallium arsenide (GaAs) and indium phosphide (InP)
- PVD, CVD and ALD thin films
- Thin films on various substrates
- Samples with multiple films or layers of different materials
- Polymers and organic films
- Metals and alloys
Ideal uses of SIMS analysis
- High-resolution elemental depth profiling
- Trace element analysis with ultra-low concentrations, including H
- Characterization of multi-layer structures and interfaces
- Failure analysis & quality control
Ask for an offer
Fill in the form, and we'll reply in one business day.
Have questions or need help? Email us at info@measurlabs.com or call our sales team.
Frequently asked questions
Static SIMS is used for elemental and isotopic characterization of surface layers in solid materials, while dynamic SIMS can be used for depth profiling, allowing elemental composition to be determined at different depths.
SIMS is only suitable for solid (typically inorganic) samples that tolerate vacuum conditions, as charged particle beams require a vacuum environment. It should also be noted that SIMS is a destructive method.
Measurlabs offers a variety of laboratory analyses for product developers and quality managers. We perform some of the analyses in our own lab, but mostly we outsource them to carefully selected partner laboratories. This way we can send each sample to the lab that is best suited for the purpose, and offer high-quality analyses with more than a thousand different methods to our clients.
When you contact us through our contact form or by email, one of our specialists will take ownership of your case and answer your query. You get an offer with all the necessary details about the analysis, and can send your samples to the indicated address. We will then take care of sending your samples to the correct laboratories and write a clear report on the results for you.
Samples are usually delivered to our laboratory via courier. Contact us for further details before sending samples.
